Which season gets the most rain?
No matter the time of year, you're bound to have seen rainfall in all seasons at least once in your lifetime.
Unless you're a farmer, in a period of drought, or live in the tropical 'wet' and 'dry' seasons, chances are you haven't really thought about the seasonal variation of rainfall.
So, let's pose it here: In what season of the year do you get the most rain?
Inspired by Brian Brettschneider, an Alaskan climatologist whose blog contains a compendium of maps of interesting weather & climate statistics mainly across North America, a map of Australia has been created that highlights the seasons of highest rainfall.
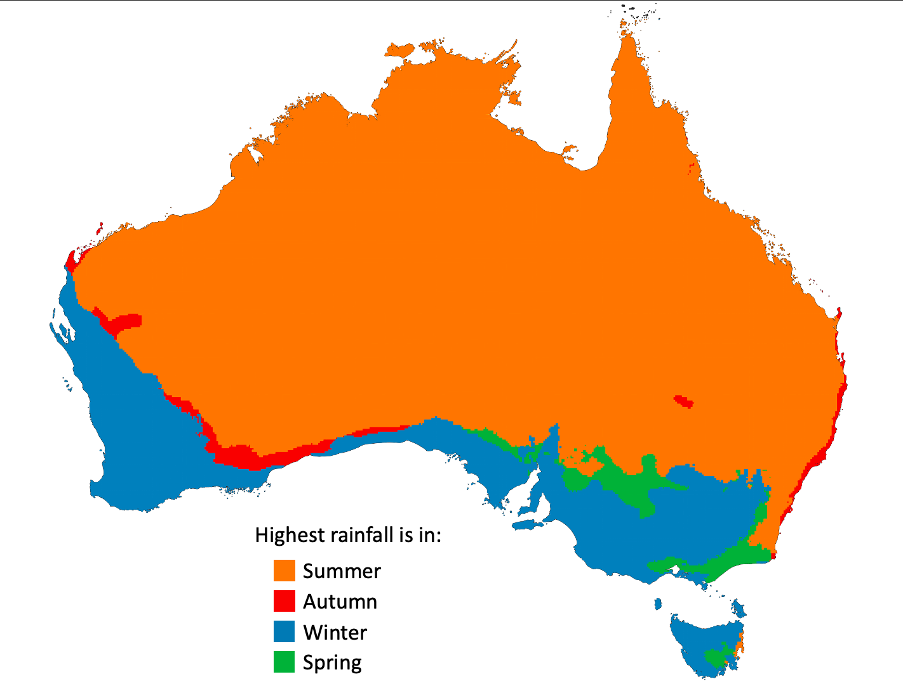
Figure: Australia's seasons with the highest rainfall based on 1991-2020 climatology (Bureau of Meteorology, 2021. Analysed using QGIS). Seasons here use the meteorological definition (e.g., 1st December - 1st February for summer, etc.)
Clearly, summertime is the major rainy ('wet') season across the northern half of Australia. As expected with the tropics, intense heat during the summer months promotes rising air (low pressure) over large regions (troughs) which form clouds that tower high into the sky and produce rain. This is much rarer inland, as the moisture source is far away, but these broad troughs can drag moisture from bodies of water and give way to precipitation.
Rainfall dominates during winter months across southern parts of Australia. Cold fronts, which are west-to-east-moving masses of cold air that can change wind direction quickly and push air upwards (low pressure), often traverse the Southern Ocean during the middle of the year. Low pressure brought about by the fronts forms bands of cloud, which produce rainy and windy conditions.
Mountain ranges have a 'drying out' effect on air that has moisture. Essentially, as moist air flows up a mountain, all the rain is released along the way, and by the time the air flows over the mountain, it is dry. This is why areas in eastern Tasmania, eastern South Australia, southeast NSW and southern Victoria do not have their peak rainfall in the peak cold front season: winter. These areas instead have a peak rainfall season in spring.
Peak rainfall is autumn is not all common; however, the populous eastern coast of Australia containing Sydney and Brisbane gives this season some significance. Generally, onshore flow has the potential to increase humidity over land and during daytime heating, this rising air can produce cloud cover and occasionally rainfall. Of all the months, onshore surface winds peak mainly in March along the east coast, with a rapid decay further inland. This narrow confinement to the coast is also shaped by the escarpment, which keeps the bulk of the rainfall to the east of the ranges.
By contrast, the seasons with the lowest rainfall have also been mapped. The winter and summer rainfalls are, for the most part, inverted. This is why coastal areas by the Bight are known for their hot, dry summers, characteristic of a Mediterranean climate (read more on the climate zones here). The 'dry' season in the north is characterised by a persistent broad high- pressure system that keeps conditions dry. Dry, offshore flow also looks to peak in springtime in the east, explaining the east coast's pockets of green.
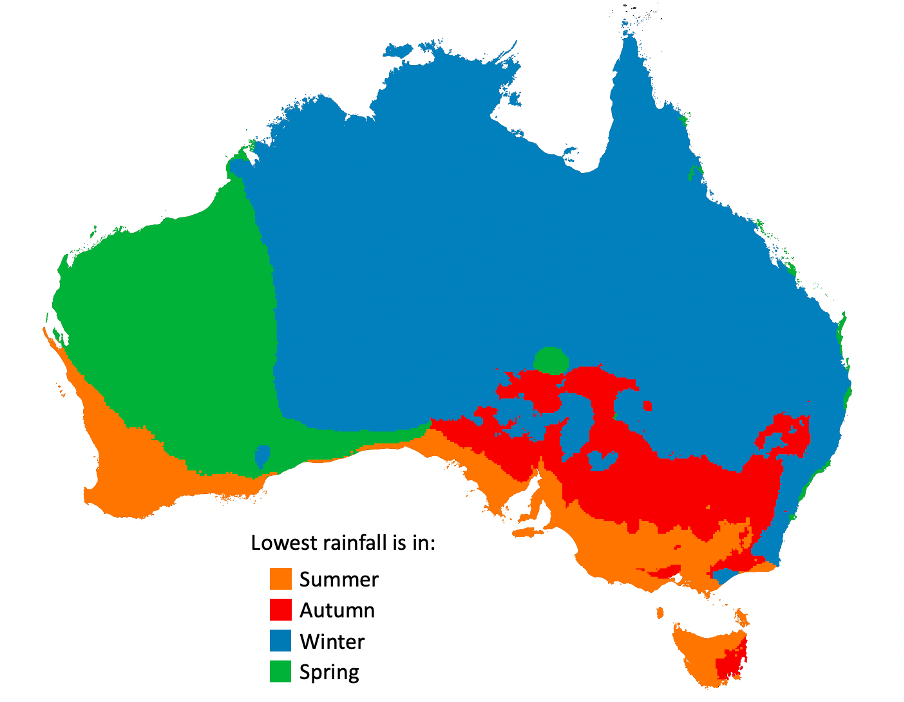
Figure: Australia's seasons with the lowest rainfall based on 1991-2020 climatology (Bureau of Meteorology, 2021. Analysed using QGIS). Seasons here use the meteorological definition.
Rainfall varies across Australia throughout the year thanks to the spreading across many latitudes and the battle between the tropical and polar influences. Be sure to keep an eye out for our forecasts and seasonal outlooks to stay informed.