July 2023 air and sea temps the hottest on record
After a month in which the record for the Earth's hottest day was shattered more than once, then the record for the Earth's hottest week melted away, is it any surprise that July 2023 turned out to be the world's hottest month on record?
News came through overnight from the Copernicus Climate Change Service – a climate monitoring body administered by the European Union – that average global air and ocean temperatures both reached record highs in July 2023.
How hot exactly?
Let's deal with air temperatures first.
- As mentioned, the global average temperature for July 2023 was the highest on record for any month, as in not just for July
- July 2023 was 0.72°C warmer than the 1991-2020 average, and 0.33°C warmer than the previous warmest month, July 2019.
- Interestingly, Copernicus estimated July 2023 to have been around 1.5°C warmer than the average for 1850-1900
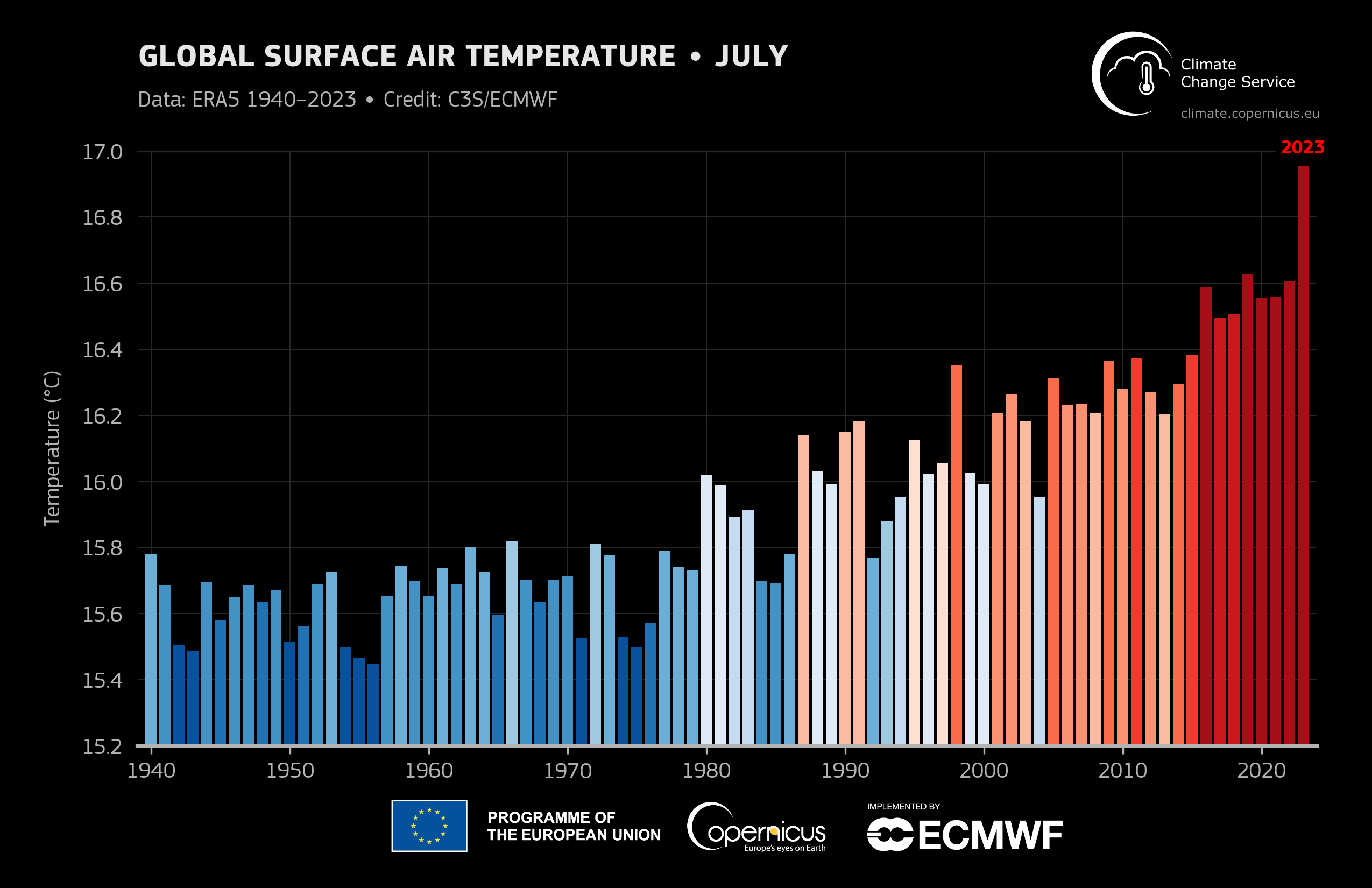
Image: Fry July. Source: Copernicus.
Now for sea temps. These often get less airtime in the discussion around human-caused global warning, but the ocean is a key part of the equation.
- For the month as a whole, global average sea surface temperatures were 0.51°C above the 1991-2020 average
- Marine heatwaves developed south of Greenland and in the Labrador Sea, in the Caribbean basin, and across the Mediterranean Sea
- The North Atlantic was 1.05°C above average in July, as we discussed in this Weatherzone story
"These records have dire consequences for both people and the planet exposed to ever more frequent and intense extreme events," Samantha Burgess, Deputy Director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service, said.
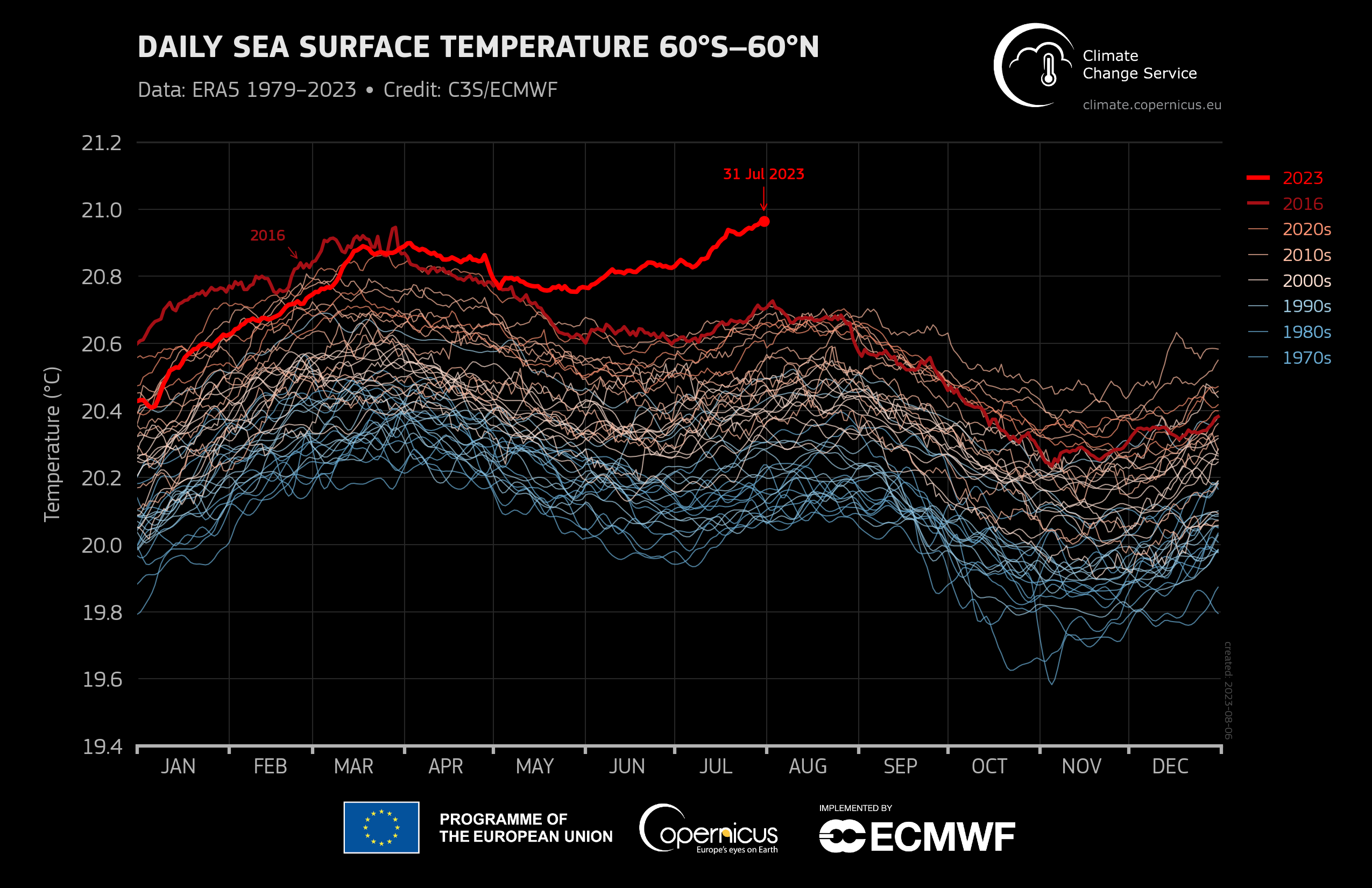
Image: The difference between 2023 and other years is dramatic. Source: Copernicus.
Meanwhile World Meteorological Organization Director of Climate Services Chris Hewitt said that the years from 2015 to 2022 were the "eight warmest years" according to readings going back at least 170 years, despite prevailing La Niña conditions in the Pacific Ocean that "tend to rein in the global average temperature and suppress them slightly".
"The long-term warming trend is driven by continued increases in concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere," he added.